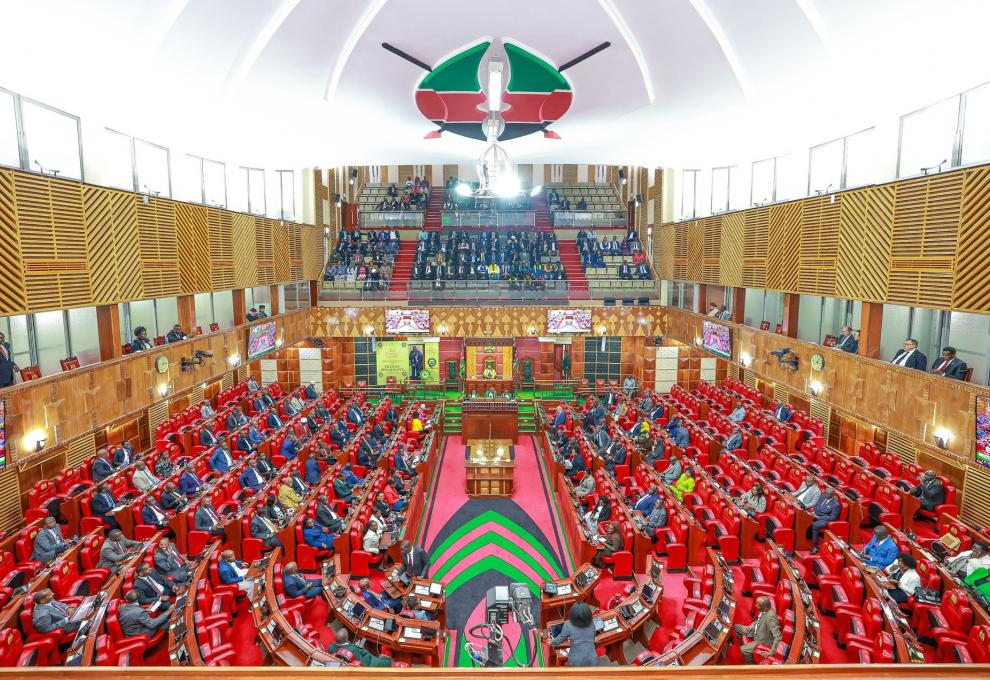
THE NATIONAL ASSEMBLY ON LONG RECESS
Bills
I. The Third Session was a markedly weighty one. During this Session, the following 29 Bills were passed by the House and assented to by H.E. the President.
A. Originating from the National Assembly
1. the Irrigation Act, 2019;
2. the County Governments Retirement Scheme Act, 2019;
3. the Statute Law (Miscellaneous Amendments) Act, 2019;
4. the Supplementary Appropriation Act, 2019;
5. the Appropriation Act, 2019;
6. the Energy Act, 2019;
7. the Petroleum Act, 2019;
8. the Physical and Land Use Planning Act, 2019;
9. the Data Protection Act, 2019;
10. the Finance Act, 2019;
11. the Parliamentary Service Commission Act, 2019;
12. the Copyright (Amendment) Act, 2019;
13. the Kenya Accreditation Service Act, 2019;
14. the Statistics (Amendment) Act, 2019;
15. the Health (Amendment) Laws Act, 2019;
16. the Division of Revenue Act, 2019;
17. the Land Value (Amendment) Act, 2019;
18. the National Cohesion and Integration (Amendment) Act, 2019;
19. the Sports (Amendment) Act, 2019;
20. the Insurance (Amendment) Act, 2019;
21. the Supplementary Appropriation (No.2) Act, 2019;
22. the Kenya Roads Board (Amendment) Act, 2019;
23. the Competition (Amendment) Bill, 2019;
24. the Insurance (Amendment)(No.2) Act, 2019; and
25. the Nuclear Regulatory Act, 2019.
B. Originating from the Senate
26. the Warehouse Receipt System Act, 2019;
27. the Urban Areas Cities (Amendment) Act, 2019;
28. the County Allocation of Revenue Act, 2019; and
29. the Assumption of the Office of the Governor Act, 2019.
President’s Veto Power
II. During this period, H.E. the President, in exercise of powers under Article 115 (1)(b) of the Constitution, by way of memoranda referred the following five Bills back to the National Assembly for reconsideration and were eventually passed having fully accommodated the reservations raised by H. E. the President–
i. The Statute Law (Miscellaneous Amendments) Bill (National Assembly Bill No.21 of 2019): regarding provisions relating the Merchant Shipping Act, No.4 of 2009 which sought to limit issues around ownership of a shipping line. The President sought to ensure that the limitations would not apply to a shipping line owned or controlled by the Government of Kenya, in this instance, the Kenya National Shipping Line (KNSL);
ii. The Finance Bill (National Assembly Bill No. 51 of 2019): specifically, the President was proposing to delete provisions relating to capping of interest rates chargeable on loans;
iii. The Parliamentary Service Bill, 2018: reservations were made regarding the role of the Salaries and Remuneration Commission;
iv. The Health Laws (Amendment) Bill, 2018: reservations were made on five of the thirteen statutes relating to the health sector that had been amended; and
v. The Insurance (Amendment) Bill, 2018: changes were recommended to some insurance-related terms, management of premiums and operations in the sector.
III. It is noteworthy that the Third Session saw an increase in the number of Private Members’ Bills totaling 52, unlike in previous sessions which had considerably less. There was only one private Members’ Bill, the Law of Contract (Amendment) Bill, 2019, which was awaiting assent, having been presented to the Presidency just before the end of 2019. It was sponsored by the Hon. Francis Waititu, MP (Juja Constituency) and was amending the Law of Contract Act so that in case of a default by the principal borrower, the creditor should first realise the assets of the principal borrower before proceeding to realise the assets of the guarantor.
IV. The year ended with several other Bills at various stages of consideration by the House as follows:
i. 20 Bills sponsored by the Leader of the Majority Party;
ii. 10 Bills sponsored by Committees; and
iii. 34 Bills from the Senate.
V. Further to this, the status of some major pending Government-sponsored Bills as at 5th December, 2019 is as follows:
|
NO. |
TITLE OF THE BILL |
STATUS |
|
A. AWAITING/UNDERGOING SECOND READING |
||
|
1. |
The Refugees Bill, 2019 |
First Reading on 10/9/2019 |
|
2. |
The Waqf Bill, 2019 |
First Reading on 6/11/2019 |
|
3. |
The County Governments (Revenue Raising Process) Bill, 2018 |
First Reading on 16/10/2018 |
|
4. |
The Business Laws (Amendment) Bill 2019 |
First Reading on 4/12/2019 |
|
B. FORWARDED TO THE SENATE |
||
|
5. |
The Government Contracts Bill, 2018 |
Forwarded to the Senate for consideration on 20/12/2018 |
|
6. |
The Statute Law (Miscellaneous Amendments) (No. 2) Bill, 2018 |
Forwarded to the Senate for consideration |
|
7. |
The Sectional Properties Bill, 2019 |
Forwarded to the Senate for consideration on 5/11/2019 |
|
8. |
The Sacco Societies (Amendment) Bill, 2018 |
Forwarded to the Senate for consideration on 5/11/2019 |
|
9. |
The National Drought Management Authority (Amendment) Bill, 2019 |
Forwarded to the Senate for consideration on 5/12/2019 |
|
C. REFERRED TO MEDIATION COMMITTEE |
||
|
10. |
The Kenya Roads Bill, 2017 |
Senate amendments rejected on 14/3/2019; Bill referred to a Mediation Committee; Mediation failed. |
|
11. |
The Public Private Partnerships (Amendment) Bill, 2017 |
Senate amendments rejected on 31/7/2019; Bill referred to a Mediation Committee; awaiting Mediation. |
|
12. |
The County Governments (Amendment) Bill (Senate Bill No. 11 of 2017) |
National Assembly amendments rejected by the Senate on 4/7/2019; Bill referred to a Mediation Committee; awaiting Mediation. |
|
13. |
The County Governments (Amendment) (No.2) Bill (Senate Bill No. 7 of 2017) |
National Assembly amendments rejected by the Senate on 30/5/2019; Bill referred to a Mediation Committee; awaiting Mediation. |
Motions and Committee reports
I. The National Assembly passed several Committee reports and Motions on diverse matters such as the transformation of Kenya Airways from a private into a publicly-owned entity; report of the Public Accounts Committee on the audited accounts of the National Government for the financial year 2016/2017, which form the basis for sharing of revenue between the two levels of government in the next financial year, Sessional Paper No. 1 of 2019 on the Policy Framework for Reforming Education and Training for Sustainable Development in Kenya, and the appointment of an external auditor to audit the Auditor-General, among others.
II. Several motions were introduced by Members on a range of topics, mainly relating to the agricultural, health, education and transport sectors.
III. The House also ratified a total of 8 international Treaties, Conventions and Agreements in line with Kenya’s membership to various regional and international bodies. These instruments ranged from a Multilateral Convention on Mutual Administrative Assistance in Tax Matters, to regional Maritime Agreements, establishment of an international Anti-Corruption Academy, an agreement on Defence Co-operation, and bilateral Air Services Agreements with various countries, among others.
IV. The National Assembly also vetted and approved nominees to several state and public offices as follows–
1. The Controller of Budget;
2. The Inspector-General of the National Police Service;
3. The Cabinet Secretary for the Ministry of Education;
4. The Chairperson and Members of the National Police Service Commission;
5. The Chairperson and Members of the National Land Commission;
6. A Member to the Salaries and Remuneration Commission;
7. The Chairperson and Members of the National Cohesion and Integration Commission;
8. Various Ambassadors and High Commissioners;
9. The Chairperson of the Kenya Fish Marketing Authority; and
10. The National Government Constituencies Development Fund Board.
Questions
V. Question Time remained popular, with a continued rise in the number of questions submitted by Members for both oral and written reply.
VI. A total of 664 questions were submitted during the Third Session. Out of these, 534 were ordinary questions, 45 were questions by private notice and 15 were for written reply by Constitutional Commissions and Independent Offices.
VII. At the close of the Session, 85 questions were still undergoing processing.
VIII. It is worth noting that Question Time as currently framed has not fully responded to Members’ wishes to fully hold the Executive to account.
Petitions
IX. Members of the public continued to petition the National Assembly directly or through Members. A total of 71 Petitions were conveyed, with 30 being concluded, 40 pending and 1 lapsing.
X. All pending petitions will proceed from the stage reached at the end of 2019, as per from the Speaker’s communication of 5th December 2019. This will ensure petitioners do not encounter difficulties in having to file their grievances repeatedly.
Highlights of the Speaker’s rulings
XI. Throughout the year, the Speaker made rulings that gave direction or guidance on several matters raised on procedure or constitutionality. Below is a highlight of some of these key rulings:
1. On Passage of the Finance Bill (National Assembly Bill No. 51 of 2019) a Second Time in terms of Article 115 of the Constitution;
2. On Determination of the Constitutionality of a Division of Revenue Bill originated by the Senate;
3. On Mandate of Audit Committees vis-à-vis that of Departmental Committees and the Place of Progress Reports in Inquiry Processes;
4. On Admissibility of the Recommendations of the Report of the Public Accounts Committee on its Examination of the Report of the Auditor General on the Financial Statements for the IEBC for the year ended 30th June 2017;
5. Appropriate Dress Code in the Chamber and in Committees;
6. On the Resolutions of County Assemblies on the Draft Punguza Mizigo (Constitution Amendment) Bill, 2019;
7. On Extension of Time Limit for Submission and Publishing of the Central Bank of Kenya’s Financial Statements and Annual Report For Financial Year 2018/2019;
8. On the Accountability of the Executive to Parliament and the Place of the Chief Administrative Secretaries in responding to Questions in the National Assembly; and
9. Guidance on Debate under the Special Motion on Approval of Revised Debt Ceiling for the National Government.
Other Milestones in 2019
The National Assembly marked some other milestones this year. Notable among these are:
XII. Translation of our Standing Orders into Kiswahili, which will hopefully entrench wider use of our second official language in the business of the House.
XIII. There was also the inaugural Parliamentary Forum for Committees which was held to showcase the role and workings of parliamentary Committees to the general public. We hope to see more Committees receive live coverage while holding their sittings in the Fourth Session.